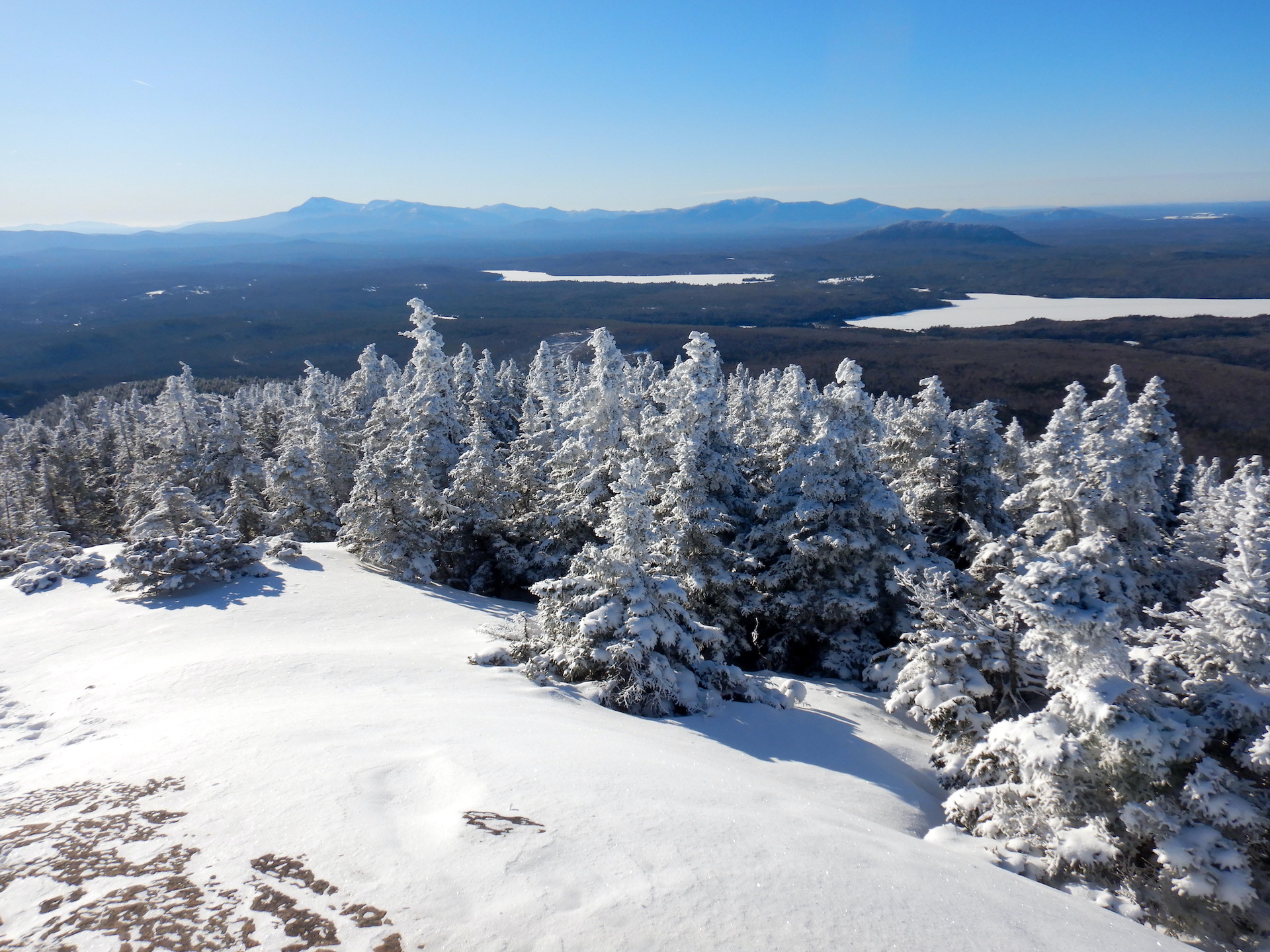
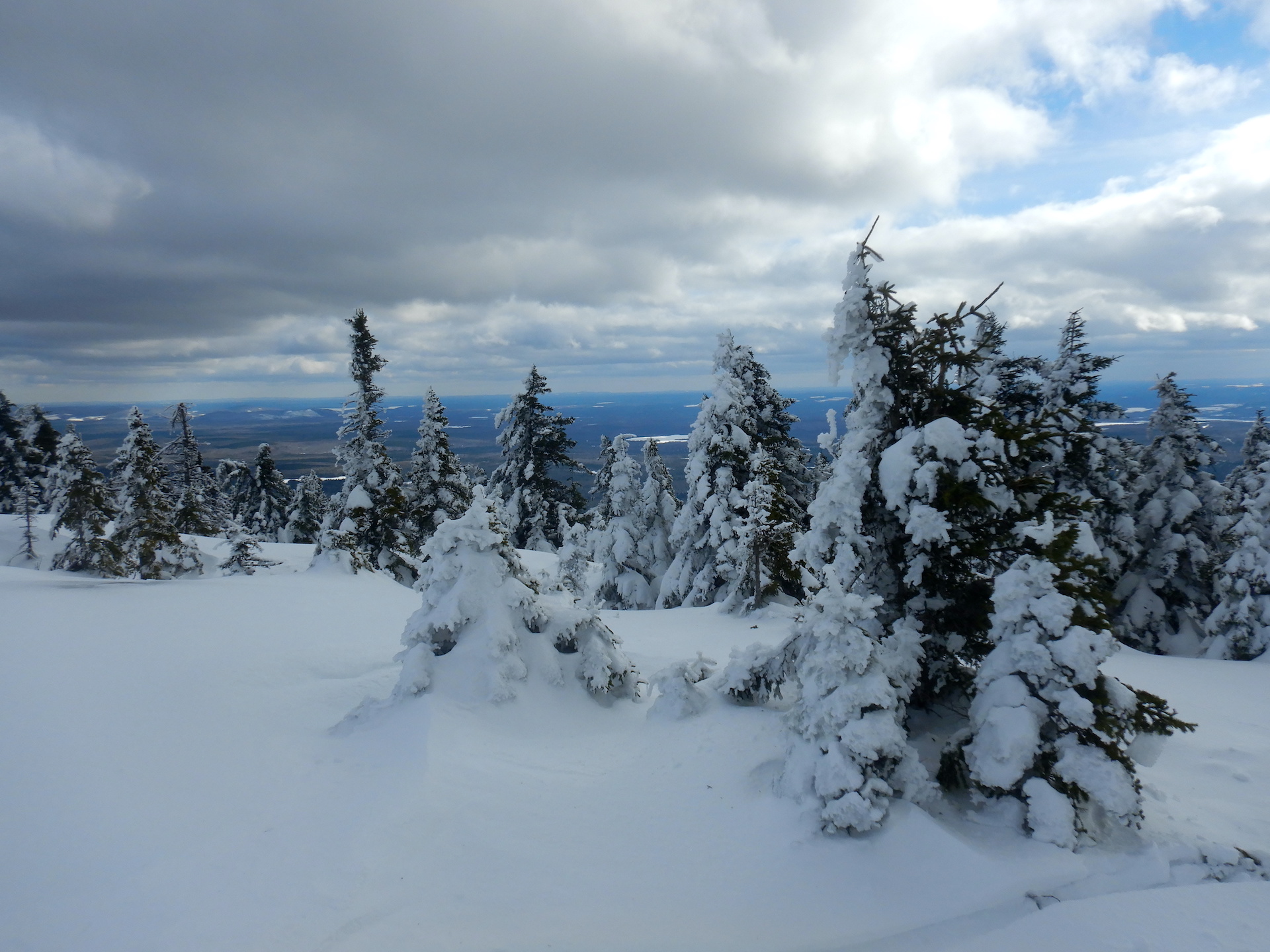
Compared to summer, winter can seem like a dull companion, especially in my corner of the globe. The buzzing of insects ceased months ago. The forest floor rests under one to three feet of snow. Trees, shrubs, invertebrates, amphibians, and fungi lie dormant. Ice insulates wetlands that were vibrating with life not long ago. Migrating birds vanished months ago. Then, there’s the dangers posed by cold weather. Numbed toes and fingers aren’t pleasant, nor are the perpetual threats of frostbite and hypothermia. All-in-all, I could convince myself that winter is a season to be endured rather than embraced. This would be a mistake, though.
While I miss the sheer volume of aliveness that accompanies summertime, winter has many endearing qualities. It helps me appreciate the abundance of summer. Off-trail travel is often easier when wetlands are frozen and snow smooths the terrain. And few experiences are as peaceful as the immense quiet that accompanies a snowstorm in an isolated grove of trees.
But this post isn’t about falling snow. Rather, it’s about a story written in the snow. Instead of looking at the wintertime forest as lonesome and empty, snow allows me to better understand how the landscape is a fully inhabited place.
Last Monday, I highlighted the travels of a fisher during More to Explore, a bi-weekly highlight show on explore.org cohosted by Brian Byrd and me.
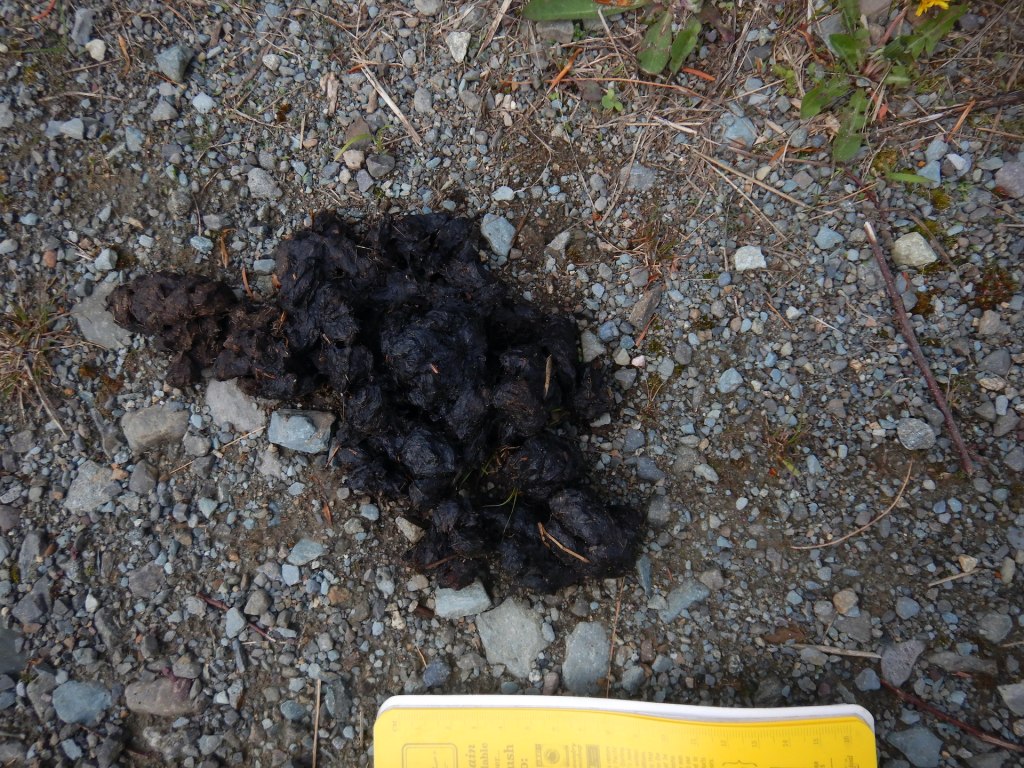
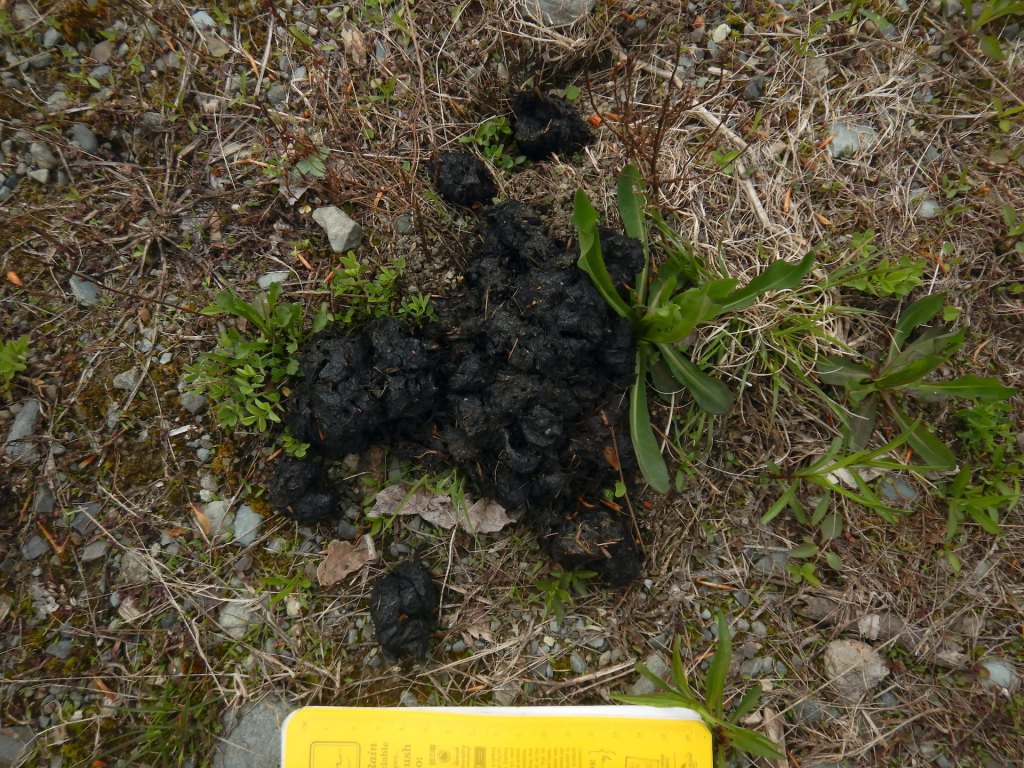
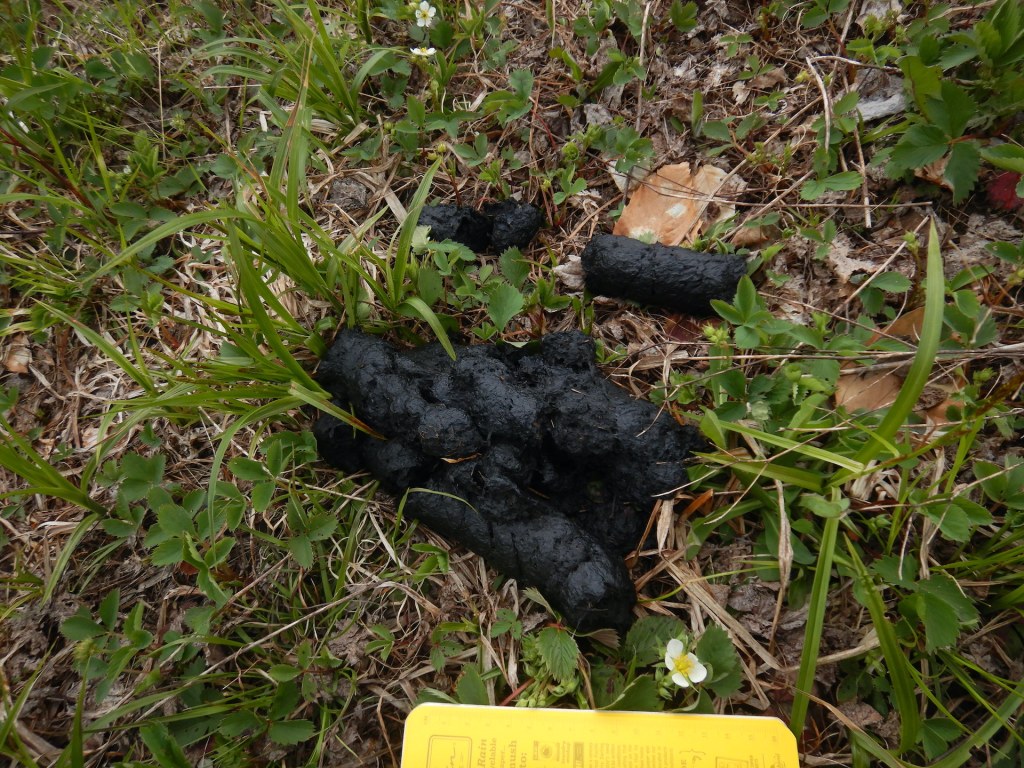
In the interest of brevity for the show, I skipped some details of the fisher’s trail. Tracking is an art that I’m still learning and I argue that I’m a slow study, but a few clues revealed I was looking at a fisher’s trail rather than a fox, coyote, marten, or lynx, all of whom inhabit the area.
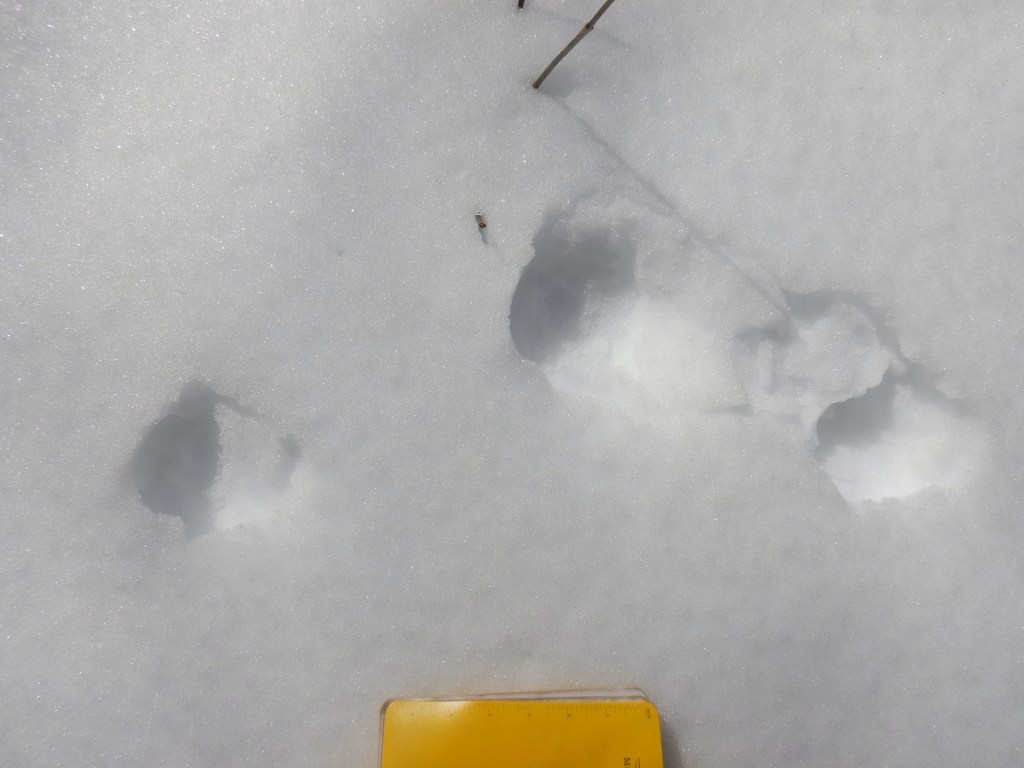
- Claw marks registered in most of the prints that I examined carefully, effectively ruling out felines since their claws are retractable and don’t register reliably in tracks.
- The clearest tracks had five toes—an important clue that rules out the canines such as foxes and coyotes. Porcupines, bears, skunks, hares, and rodents can make five-toed tracks too, but they have other features that make them distinctive.*
- The tracks’ size were too large for other members of the weasel family who live here such as short- and long-tailed weasels, mink, and marten. I could rule out river otters too since there was no evidence that the animal slid across the snow (something otters routinely do) or sought liquid water. The trackway crossed a beaver-created swamp but the tracks did not lead to water as an otter would have.
- The animal’s gait was a mostly loping in a 3 x 4 pattern, which is a common way for fishers to travel. The 3 x 4 lope is a method of travel where a fisher places a front and rear foot from one side of the body in the same place, while the feet on the other side do not overlap. This gives the impression of only three tracks instead of four. Fishers walk, lope in a 2 x 2 pattern, and gallop too, but in my experience they’ll use a 3 x 4 pattern much more often in firm snow than American martens.
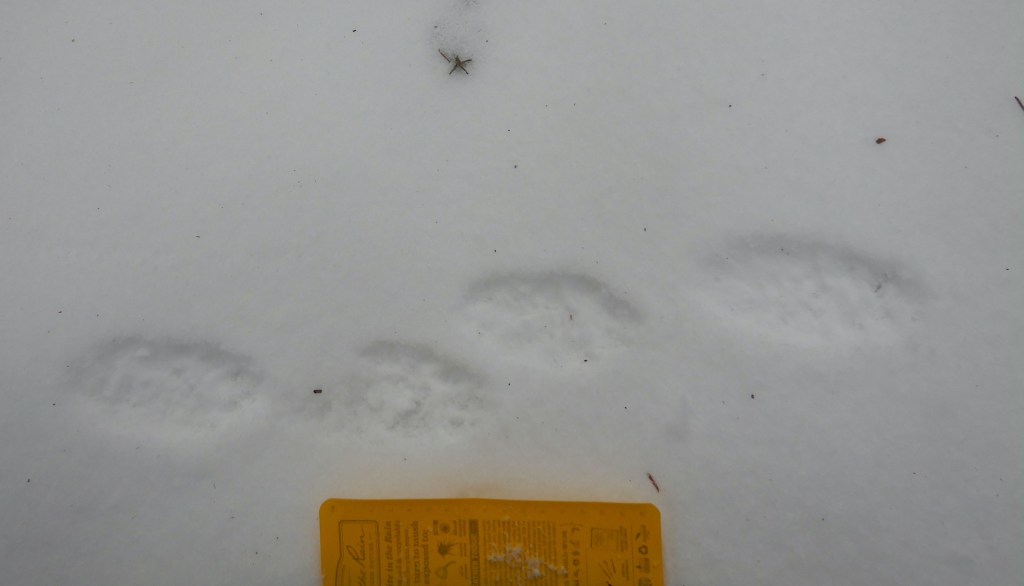
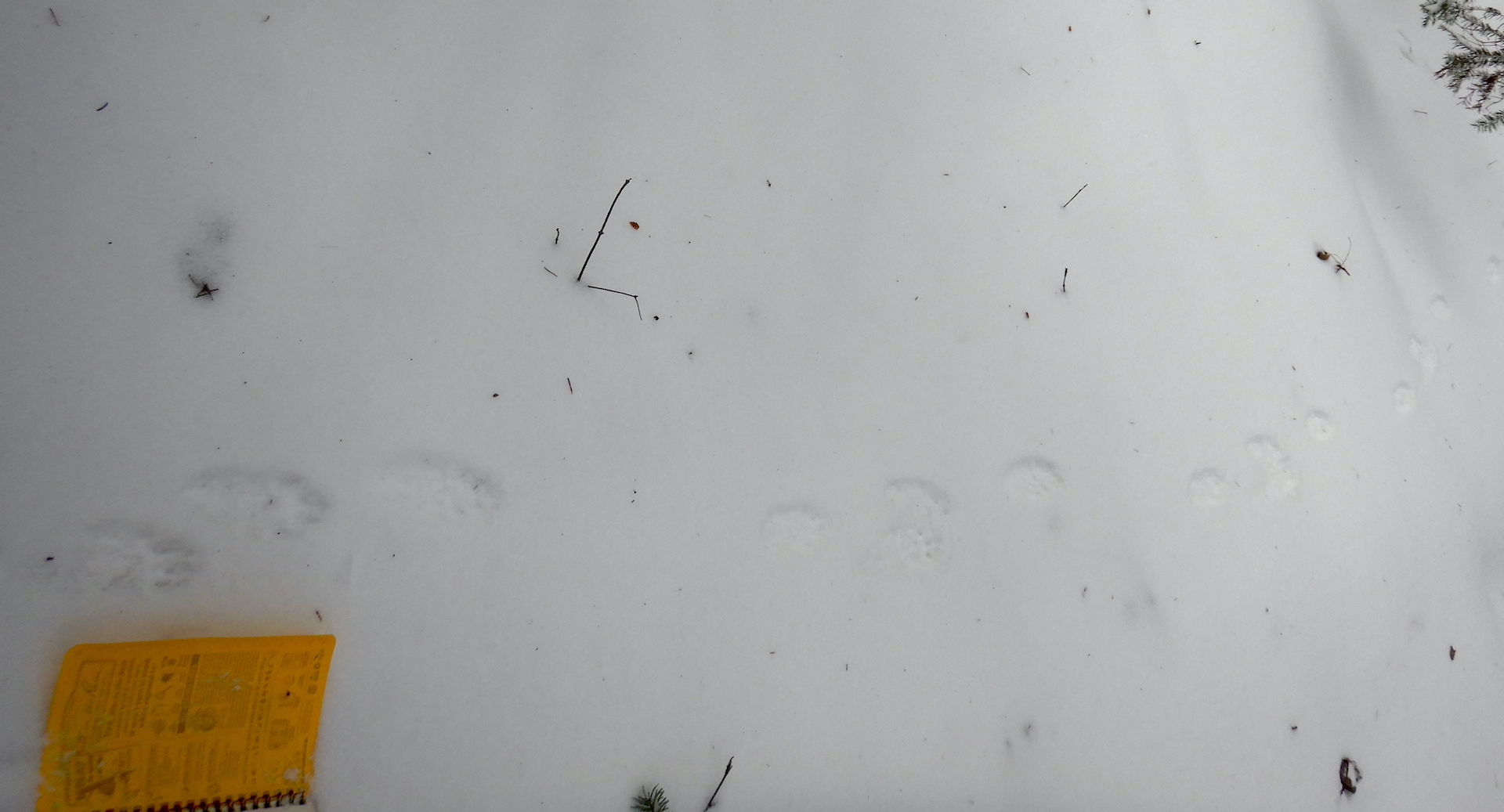


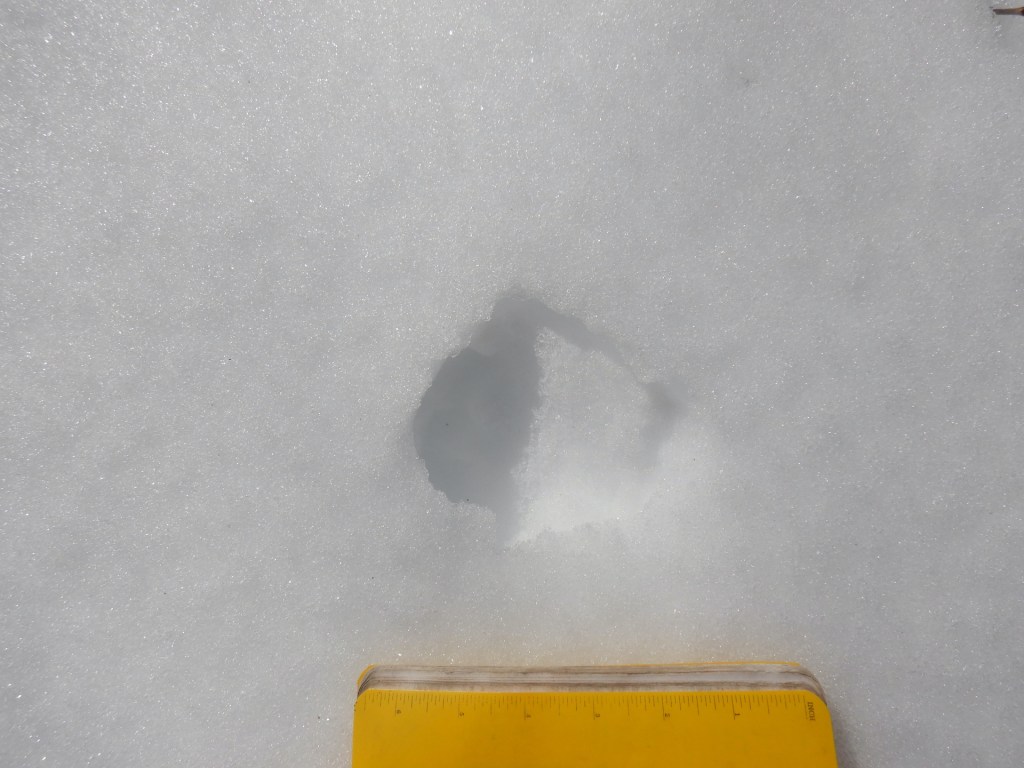
Several other mammals were active that day as well. Snowshoe hares, red fox, red squirrels, mice, and voles all left tracks or scat to reveal their presence. I was only lucky enough to be chastised by a couple of squirrels and didn’t see any other mammals for the majority of the day but walking slowly and quietly gives one the opportunity to be surprised. In a moment of quiet contemplation, the kind you experience while gazing through trees pondering your next move, a glimmer of movement appeared in the corner of my eye. I turned my head to find a weasel bounding through the snow. I didn’t dare reach for my camera knowing I’d spook it into hiding, although I remember clearly my confusion upon seeing it.
A long-tailed weasel changes its fur color from summer brown to winter white and back again with the seasons. In winter, they are nearly pure white except for the tip of their tail, which is black—a feature that seems to misdirect attacking predators away from the head. This weasel, however, appeared to have a dark tail and head.
My brain needed to register a few more bounds by the weasel to clear the confusion. it wasn’t oddly colored. The weasel was carrying a vole or mouse in his mouth. As he disappeared in a thicket, I was offered a special opportunity to examine its prints for clues about that may help me better understand how small weasels move in snow when they are burdened by the weight of their prey.
Long-tailed weasels and the smaller short-tailed weasel (ermine) travel most often in snow by using a 2 x 2 lope. When you see them traveling in this way, it looks almost like a long hop, with the front feet hitting the ground first. The front feet quickly lift into the air while the hind feet land in the same place. The weasel I watched used this method and he seemed to carry his rodent cargo with ease—an impressive display of relative strength. His prey, though, left an important clue. Each of the weasel’s bounds were accompanied by a slash in the snow, which must have been created by part of the dead rodent (a foot? a tail?) dragging in the snow with each leap of the weasel.


As I discussed in the video segment above, the life of a fisher would be far more mysterious without the record it leaves in snow. I would have no real clue how much fishers leave scent marks or climb trees without reading their trackways. Likewise, if I’d not been in the right place at the right time or been looking in a different direction I would have missed the weasel and its meal completely. Had I stumbled upon its trail with the strange, repeating mark next to each print I’m not sure I’d reason it was from the weasel’s prey. But now, I’ll be looking for other examples like it.
I hope you have the opportunity to utilize snow to learn more about your neighbors. When the snow pack melts in spring, I welcome the change although I must admit that forest seems a bit lonelier when I don’t know who has been visiting.
*Mammal Tracks and Sign: A Guide to North American Species by Mark Elbroch is an invaluable resource if you want to learn more.